Tricks,Tips, Tweaks of Embedded C, C, Micro-controllers, Peripherals, Compilers, Datasheets, Linux, RTOS and Embedded Communication Protocols.
Pages1
Setting Static IP in Ubuntu Desktop: Using /etc/network/interfaces
To
change IP to static using: /etc/network/interfaces
Step 1: Open /etc/network/interfaces /* Login as super user to execute this */
/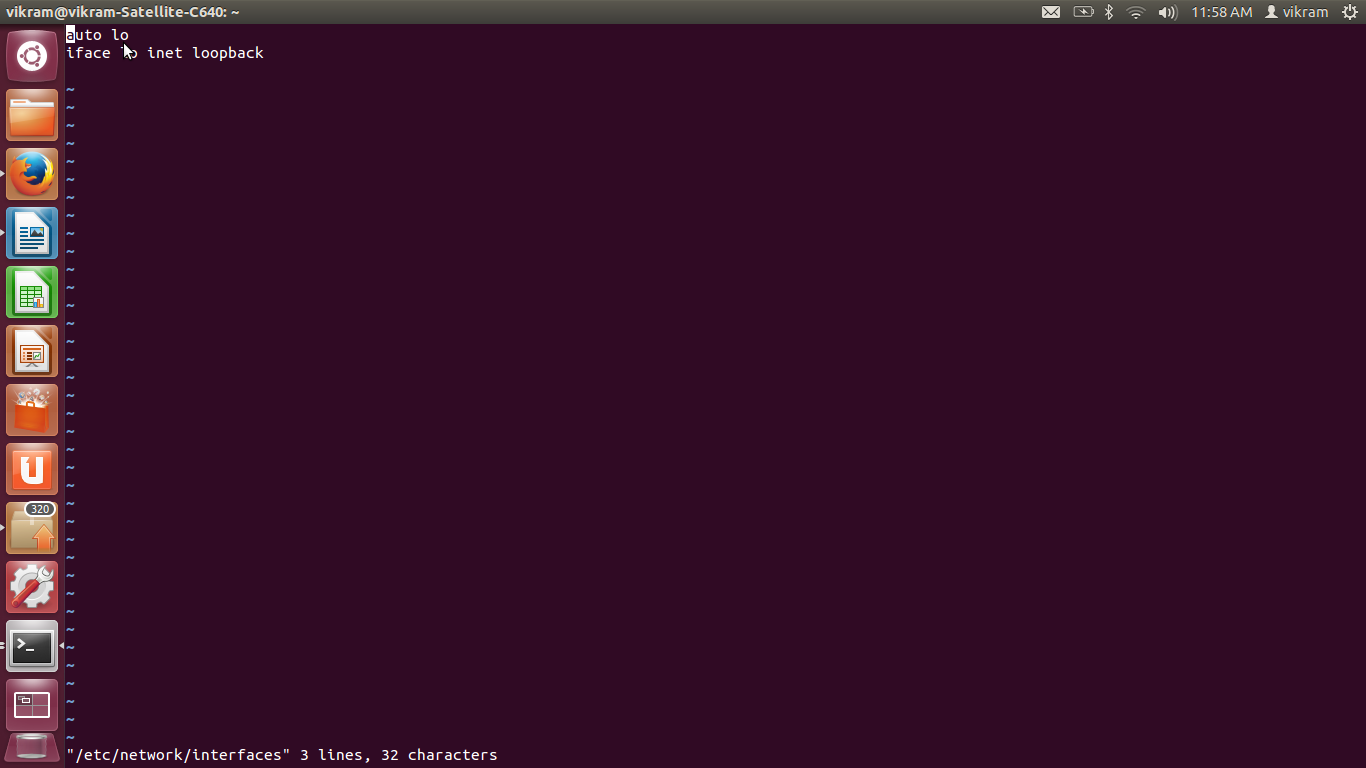
Step 2: Enter below details in file
----------------------------------------------------------
Note: To change this to Dynamic IP again please follow reverse process step4 to be run as it is.
Step 1: Open /etc/network/interfaces /* Login as super user to execute this */
/

Step 2: Enter below details in file
----------------------------------------------------------
auto eth0iface eth0 inet staticaddress 192.168.1.1 /* Address u want */netmask 255.255.255.0 /* Subnet mask */gateway 192.168.1.1 /* Default mask */
-------------------------------------------------------Step 3:
Save above changesStep 4:/etc/init.d/networking restartto Restart service with static IP
Note: To change this to Dynamic IP again please follow reverse process step4 to be run as it is.
Playing with services in UBUNTU; Debugging a service in UBUNTU
Lets take example of
service called "ssh" used for initiating secure connection
with remote machine.
To collect debug logs in case of ssh please execute;
ssh -vvv hostname@ ipaddres
sftp -vvv hostname@ ipaddres you will get lot of logs
To check status of a service
$ sudo status service ssh /* will show you status of service*/
OR
OR
OR
To collect debug logs in case of ssh please execute;
ssh -vvv hostname@ ipaddres
sftp -vvv hostname@ ipaddres you will get lot of logs
To check status of a service
$ sudo status service ssh /* will show you status of service*/
Ubuntu Linux: To Start OpenSSH Server;Execute below command
$
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh startor$
sudo service ssh startUbuntu Linux: Stop OpenSSH server
Type the following command:$
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh stopOR
$
sudo service ssh stopUbuntu Linux: Restart OpenSSH server
Type the following command:$
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restartOR
$
sudo service ssh restartUbuntu Linux: See status of OpenSSH server
Type the following command:$
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh statusOR
$
sudo service ssh statusNote:
sftp,scp
always make ssh connection. Command to check UBUNTU( Diribution -specific release) version
Command is :
$lsb_release -a
lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 12.04.4 LTS
Release: 12.04
Codename: precise
$ man lsb_release(1)
NAME
lsb_release - print distribution-specific information
SYNOPSIS
lsb_release [options]
DESCRIPTION
The lsb_release command provides certain LSB (Linux Standard Base) and distribution-specific information.
If no options are given, the -v option is assumed.
OPTIONS
The program follows the usual GNU command line syntax, with long options starting with two dashes (`--'). A summary of
options are included below.
-v, --version
Show the version of the LSB against which your current installation is compliant. The version is expressed as a
colon separated list of LSB module descriptions.
-i, --id
Display the distributor's ID.
-d, --description
Display a description of the currently installed distribution.
-r, --release
Display the release number of the currently installed distribution.
-c, --codename
Display the code name of the currently installed distribution.
-a, --all
Display all of the above information.
-s, --short
Use the short output format for any information displayed. This format omits the leading header(s).
-h, --help
Show summary of options.
NOTES
This is a reimplementation of the lsb_release command provided by the Free Standards Group. Any bugs are solely the
responsibility of the author below.
Detection of systems using a mix of packages from various distributions or releases is something of a black art; the cur‐
rent heuristic tends to assume that the installation is of the earliest distribution which is still being used by .B apt
but that heuristic is subject to error.
SEE ALSO
lsb(8)
-------------------------------------------------------------------
$lsb_release -a
lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 12.04.4 LTS
Release: 12.04
Codename: precise
$ man lsb_release(1)
NAME
lsb_release - print distribution-specific information
SYNOPSIS
lsb_release [options]
DESCRIPTION
The lsb_release command provides certain LSB (Linux Standard Base) and distribution-specific information.
If no options are given, the -v option is assumed.
OPTIONS
The program follows the usual GNU command line syntax, with long options starting with two dashes (`--'). A summary of
options are included below.
-v, --version
Show the version of the LSB against which your current installation is compliant. The version is expressed as a
colon separated list of LSB module descriptions.
-i, --id
Display the distributor's ID.
-d, --description
Display a description of the currently installed distribution.
-r, --release
Display the release number of the currently installed distribution.
-c, --codename
Display the code name of the currently installed distribution.
-a, --all
Display all of the above information.
-s, --short
Use the short output format for any information displayed. This format omits the leading header(s).
-h, --help
Show summary of options.
NOTES
This is a reimplementation of the lsb_release command provided by the Free Standards Group. Any bugs are solely the
responsibility of the author below.
Detection of systems using a mix of packages from various distributions or releases is something of a black art; the cur‐
rent heuristic tends to assume that the installation is of the earliest distribution which is still being used by .B apt
but that heuristic is subject to error.
SEE ALSO
lsb(8)
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


